Authors:
(1) Simon R. Davies, School of Computing, Edinburgh Napier University, Edinburgh, UK (s.davies@napier.ac.uk);
(2) Richard Macfarlane, School of Computing, Edinburgh Napier University, Edinburgh, UK;
(3) William J. Buchanan, School of Computing, Edinburgh Napier University, Edinburgh, UK.
Table of Links
- Abstract and 1 Introduction
- 2. Related Work
- 3. Methodology and 3.1. File Content Analysis
- 3.2. File Name Analysis
- 3.3. Executable Analysis
- 3.4. Behaviour Analysis
- 4. Evaluation and Discussion
- 4.1. Majority Voting
- 5. Conclusion
- 5.1. Limitations
- 5.2. Future Work
- References and Appendix
References
[1] Abbasi, M.S., Al-Sahaf, H., Welch, I., 2021. Automated Behaviorbased Malice Scoring of Ransomware Using Genetic Programming. 2021 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, SSCI 2021 - Proceedings doi:10.1109/SSCI50451.2021.9660009.
[2] Ahmed, M.E., Kim, H., Camtepe, S., Nepal, S., 2021. Peeler: Profiling Kernel-Level Events to Detect Ransomware. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 12972 LNCS, 240– 260. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-88418-5\_12, arXiv:2101.12434.
[3] Ahmed, Y.A., Koçer, B., Al-Rimy, B.A.S., 2020. Automated Analysis Approach for the Detection of High Survivable Ransomware. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems 14, 2236–2257. doi:10.3837/tiis.2020.05.021.
[4] Al-rimy, B.A.S., Maarof, M.A., Shaid, S.Z.M., 2019. Cryptoransomware early detection model using novel incremental bagging with enhanced semi-random subspace selection. Future Generation Computer Systems 101, 476–491. URL: https://doi.org/10.1016/j. future.2019.06.005, doi:10.1016/j.future.2019.06.005.
[5] Alam, M., Sinha, S., Bhattacharya, S., Dutta, S., Mukhopadhyay, D., Chattopadhyay, A., 2020. RAPPER: Ransomware Prevention via Performance Counters. Arxiv , 1–18URL: http://arxiv.org/abs/2004. 01712, arXiv:2004.01712.
[6] Andronio, N., Zanero, S., Maggi, F., 2015. HelDroid: Dissecting and Detecting Mobile Ransomware, in: Bos, H., Monrose, F., Blanc, G. (Eds.), Research in Attacks, Intrusions, and Defenses, Springer International Publishing, Cham. pp. 382–404.
[7] Balogh, Š., Pondelik, M., 2011. Capturing encryption keys for digital analysis. Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications, IDAACS’2011 2, 759–763. doi:10.1109/IDAACS.2011.6072872.
[8] Berrueta, E., Morato, D., Magana, E., Izal, M., 2019. A Survey on Detection Techniques for Cryptographic Ransomware. IEEE Access 7, 144925–144944. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2945839.
[9] Bottazzi, G., Italiano, G., Spera, D., Bottazzi, G., Italiano, G., Spera, D., Ransomware, P., Through, A., Bottazzi, G., Italiano, G.F., Spera, D., 2018. Preventing Ransomware Attacks Through File System Filter Drivers, in: Proceedings of the Second Italian Conference on Cyber Security (ITASEC18), p. 4. URL: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323125541_ Preventing_Ransomware_Attacks_Through_File_System_Filter_Drivers.
[10] Buchanan, . Digital Forensics Magic Numbers. URL: https:// asecuritysite.com/forensics/magic, (Last Accessed: 2022-10-20).
[11] Chadha, S., Kumar, U., 2017. Ransomware: Let’s fight back!, in: 2017 International Conference on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA), pp. 925–930. doi:10.1109/CCAA.2017.8229926.
[12] Choudhury, P., Kumar, K.R., Nandi, S., Athithan, G., 2019. An empirical approach towards characterization of encrypted and unencrypted VoIP traffic. Multimedia Tools and Applications 79, 603– 631. doi:10.1007/s11042-019-08088-w.
[13] Continella, A., Guagnelli, A., Zingaro, G., De Pasquale, G., Barenghi, A., Zanero, S., Maggi, F., 2016. ShieldFS: A self-healing, ransomware-aware file system, in: Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Conference on Computer Security Applications, pp. 336–347. URL: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/2991079.2991110, doi:10.1145/ 2991079.2991110.
[14] Dargahi, T., Dehghantanha, A., Bahrami, P.N., Conti, M., Bianchi, G., Benedetto, L., 2019. A Cyber-Kill-Chain based taxonomy of crypto-ransomware features. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques 15, 277–305. URL: https://doi.org/10.1007/ s11416-019-00338-7, doi:10.1007/s11416-019-00338-7.
[15] Davies, S.R., Macfarlane, R., Buchanan, W.J., 2021a. Differential area analysis for ransomware attack detection within mixed file datasets. Computers and Security 108, 102377. URL: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102377, doi:10.1016/j. cose.2021.102377, arXiv:2106.14418.
[16] Davies, S.R., Macfarlane, R., Buchanan, W.J., 2021b. NapierOne. URL: www.napierone.com.
[17] Davies, S.R., Macfarlane, R., Buchanan, W.J., 2022a. Comparison of Entropy Calculation Methods for Ransomware Encrypted File Identification. Entropy 24. doi:10.3390/e24101503.
[18] Davies, S.R., Macfarlane, R., Buchanan, W.J., 2022b. NapierOne: A modern mixed file data set alternative to Govdocs1. Forensic Science International: Digital Investigation 40, 301330. URL: https://doi. org/10.1016/j.fsidi.2021.301330, doi:10.1016/j.fsidi.2021.301330.
[19] De Gaspari, F., Hitaj, D., Pagnotta, G., De Carli, L., Mancini, L.V., 2020. The Naked Sun: Malicious Cooperation Between Benign-Looking Processes. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 12147 LNCS, 254–274. doi:10.1007/ 978-3-030-57878-7\_13, arXiv:1911.02423.
[20] De Gaspari, F., Hitaj, D., Pagnotta, G., De Carli, L., Mancini, L.V., 2022. Evading behavioral classifiers: a comprehensive analysis on evading ransomware detection techniques. Neural Computing and Applications 34, 12077–12096. URL: https://doi.org/10.1007/ s00521-022-07096-6, doi:10.1007/s00521-022-07096-6.
[21] Dutta, N., Jadav, N., Tanwar, S., Sarma, H.K.D., Pricop, E., 2022. Introduction to Malware Analysis. Springer Singapore, Singapore. chapter Introducti. pp. 129–141. URL: https://doi.org/10.1007/ 978-981-16-6597-4_7, doi:10.1007/978-981-16-6597-4\_7.
[22] F.R.S., K.P., 2009. X. On the criterion that a given system of deviations from the probable in the case of a correlated system of variables is such that it can be reasonably supposed to have arisen from random sampling. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786440009463897 50, 157–175. URL: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/ 14786440009463897, doi:10.1080/14786440009463897.
[23] Ganfure, G.O., Wu, C.F., Chang, Y.H., Shih, W.K., 2020. DeepGuard: Deep Generative User-behavior Analytics for Ransomware Detection. Proceedings - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics, ISI 2020 doi:10.1109/ISI49825. 2020.9280508.
[24] Genç, Z.A., Lenzini, G., Ryan, P.Y., 2018. No random, no ransom: A key to stop cryptographic ransomware. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 10885 LNCS, 234–255. doi:10. 1007/978-3-319-93411-2\_11.
[25] Genç, Z.A., Lenzini, G., Ryan, P.Y.A., 2019. NoCry : No More Secure Encryption Keys for Cryptographic Ransomware, in: International Workshop on Emerging Technologies for Authorization and Authentication, pp. 69–85. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-39749-4\_5.
[26] Gharib, A., Ghorbani, A., 2017. DNA-Droid: A real-time android ransomware detection framework. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 10394 LNCS, 184–198. doi:10. 1007/978-3-319-64701-2\_14.
[27] Google, 2015. File types indexable by Google. URL: https:// support.google.com/webmasters/answer/35287?hl=en, (Last Accessed: 2021-03-24).
[28] Halderman, J.A., Schoen, S.D., Heninger, N., Clarkson, W., Paul, W., Calandrino, J.A., Feldman, A.J., Appelbaum, J., Felten, E.W., 2009. Lest we remember: Cold-boot attacks on encryption keys. Communications of the ACM 52, 91–98. doi:10.1145/1506409.1506429.
[29] Hall, G.A., 2006. Sliding Window Measurement for File Type Identification. Proceedings of the 1997 ACM symposium on Applied computing , 529–532.
[30] Heninger, N., Feldman, A., 2008. AESKeyFind. URL: https://github.com/eugenekolo/sec-tools/tree/master/crypto/ aeskeyfind/aeskeyfind.
[31] Homayoun, S., Dehghantanha, A., Ahmadzadeh, M., Hashemi, S., Khayami, R., 2020. Know Abnormal, Find Evil: Frequent Pattern Mining for Ransomware Threat Hunting and Intelligence. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing 8, 341–351. doi:10. 1109/TETC.2017.2756908.
[32] John, T.C., Abbasi, M.S., Al-Sahaf, H., Welch, I., 2022. Automatically Evolving Malice Scoring Models through Utilisation of Genetic Programming: A Cooperative Coevolution Approach. volume 1. john ed., Association for Computing Machinery. doi:10.1145/3520304. 3529063.
[33] Joseph, P., Norman, J., 2020. Systematic Memory Forensic Analysis of Ransomware using Digital Forensic Tools. International Journal of Natural Computing Research 9, 61–81. doi:10.4018/ijncr. 2020040105.
[34] Kara, I., 2023. Fileless malware threats: Recent advances, analysis approach through memory forensics and research challenges. Expert Systems with Applications 214, 119133. URL: https: //www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417422021510, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119133.
[35] Kessler, G., . GCK’S File Signature Table. URL: https://www.garykessler.net/library/file_sigs.html, (Last Accessed: 2023-02-10).
[36] Kharaz, A., Arshad, S., Mulliner, C., Robertson, W., Mulliner, C., Robertson, W., 2016. UNVEIL : A Large-Scale , Automated Approach to Detecting Ransomware This paper is included in the Proceedings of the. In Proceedings of the 2014 VIRUS BULLETIN CONFERENCE , 757– 772URL: https://www.usenix.org/conference/usenixsecurity16/ technical-sessions/presentation/kharaz.
[37] Kharraz, A., Kirda, E., 2017a. Redemption: Real-Time Protection Against Ransomware at End-Hosts. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 10453 LNCS, 98–119. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-66332-6\_5.
[38] Kharraz, A., Kirda, E., 2017b. Redemption: Real-Time Protection Against Ransomware at End-Hosts. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 10453 LNCS, 98–119. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-66332-6\_5.
[39] Ki, Y., Kim, E., Kim, H.K., 2015. A novel approach to detect malware based on API call sequence analysis. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks 2015. URL: https://journals.sagepub. com/doi/pdf/10.1155/2015/659101, doi:10.1155/2015/659101.
[40] Kim, G.Y., Paik, J.Y., Kim, Y., Cho, E.S., 2022. Byte Frequency Based Indicators for Crypto-Ransomware Detection from Empirical Analysis. Journal of Computer Science and Technology 37, 423–442. doi:10.1007/s11390-021-0263-x.
[41] Klein, T., 2006. All your private keys are belong to us process memory. Tech. Rep , 1–7URL: https://citeseerx.ist.psu. edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi\protect\@normalcr\relax= cf85042cca0da125b860db7c2fefb38012396cbc.
[42] Kornblum, J., 2017. findaes. URL: http://jessekornblum.com/tools/ findaes/, (Last Accessed: 2019-08-10).
[43] Lebbie, M., Prabhu, S.R., Agrawal, A.K., 2022. Comparative Analysis of Dynamic Malware Analysis Tools, in: Dua, M., Jain, A.K., Yadav, A., Kumar, N., Siarry, P. (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Paradigms of Communication, Computing and Data Sciences, Springer Singapore, Singapore. pp. 359–368.
[44] Lee, J., Lee, K., 2022. A Method for Neutralizing Entropy Measurement-Based Ransomware Detection Technologies Using Encoding Algorithms. Entropy 24. doi:10.3390/e24020239.
[45] Lee, K., Lee, S.Y., Yim, K., 2019a. Effective Ransomware Detection Using Entropy Estimation of Files for Cloud Services, in: I-SPAN 2019: Pervasive Systems, Algorithms and Networks, Springer International Publishing. pp. 133–139. URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/ 978-3-030-30143-9_11, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-30143-9\_11.
[46] Lee, K., Lee, S.Y., Yim, K., 2019b. Machine Learning Based File Entropy Analysis for Ransomware Detection in Backup Systems. IEEE Access 7, 110205–110215. URL: https://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ ACCESS.2019.2931136, doi:10.1109/access.2019.2931136.
[47] Lemmou, Y., Lanet, J.L., Souidi, E.M., 2021. In-depth analysis of ransom note files. Computers 10, 1–25. doi:10.3390/computers10110145.
[48] Leommoore, . File Magic Numbers · GitHub. URL: https: //gist.github.com/leommoore/f9e57ba2aa4bf197ebc5, (Last Accessed: 2023-02-28).
[49] Li, W.J., Wang, K., Stolfo, S.J., Herzog, B., 2005. Fileprints: Identifying file types by n-gram analysis. Proceedings from the 6th Annual IEEE System, Man and Cybernetics Information Assurance Workshop, SMC 2005 2005, 64–71. URL: https://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ IAW.2005.1495935, doi:10.1109/IAW.2005.1495935.
[50] Lokuketagoda, B., Weerakoon, M.P., Kuruppu, U.M., Senarathne, A.N., Yapa Abeywardena, K., 2018. R - Killer: An email based ransomware protection tool. 13th International Conference on Computer Science and Education, ICCSE 2018 , 735–741doi:10.1109/ICCSE. 2018.8468807.
[51] Maartmann-Moe, C., Thorkildsen, S.E., Årnes, A., 2009. The persistence of memory: Forensic identification and extraction of cryptographic keys. DFRWS 2009 Annual Conference 6, 132–140. doi:10. 1016/j.diin.2009.06.002.
[52] Maigida, A.M., Abdulhamid, S.M., Olalere, M., Alhassan, J.K., Chiroma, H., Dada, E.G., 2019. Systematic literature review and metadata analysis of ransomware attacks and detection mechanisms. Journal of Reliable Intelligent Environments 5, 67–89. URL: https://doi. org/10.1007/s40860-019-00080-3, doi:10.1007/s40860-019-00080-3.
[53] MalwareBytes, 2023. ION starts bringing customers back online after LockBit ransomware attack. URL: https://www.malwarebytes.com/blog/news/2023/02/ ion-starts-bringing-customers-back-online-after-lockbit-ransomware-attack, (Last Accessed: 2023-02-20).
[54] Manavi, F., Hamzeh, A., 2022. A novel approach for ransomware detection based on PE header using graph embedding. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques URL: https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11416-021-00414-x, doi:10.1007/s11416-021-00414-x.
[55] McDonald, G., Papadopoulos, P., Pitropakis, N., Ahmad, J., Buchanan, W.J., 2022. Ransomware: Analysing the Impact on Windows Active Directory Domain Services. Sensors 22. doi:10.3390/ s22030953, arXiv:2202.03276.
[56] McIntosh, T., Jang-Jaccard, J., Watters, P., Susnjak, T., 2019. The Inadequacy of Entropy-Based Ransomware Detection, in: International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Springer International Publishing. pp. 181–189. URL: https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/ 978-3-030-36802-9_20, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-36802-9\_20.
[57] Mehnaz, S., Mudgerikar, A., Bertino, E., 2018. RWGuard: A Real-Time Detection System Against Cryptographic Ransomware, in: International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions, and Defenses. Springer International Publishing. volume 1, pp. 114– 136. URL: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00470-5_6, doi:10. 1007/978-3-030-00470-5\_6.
[58] Moser, A., Kruegel, C., Kirda, E., 2007. Limits of Static Analysis for Malware Detection, in: Twenty-Third Annual Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC 2007), pp. 421–430. doi:10.1109/ ACSAC.2007.21.
[59] Nieuwenhuizen, D., 2017. A behavioural-based approach to ransomware detection. Computer Science URL: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/ A-behavioural-based-approach-to-ransomware-Nieuwenhuizen93b6e2fdf2a79608e44ab64
[60] O’Kane, P., Sezer, S., McLaughlin, K., 2011. Obfuscation: The Hidden Malware. IEEE Security & Privacy 9, 41–47. doi:10.1109/MSP. 2011.98.
[61] Oz, H., Aris, A., Levi, A., Uluagac, A.S., 2021. A Survey on Ransomware: Evolution, Taxonomy, and Defense Solutions. ACM Computing Surveys 1. URL: http://arxiv.org/abs/2102.06249, arXiv:2102.06249.
[62] Pattern Recognition and Applications Lab, 2023. R-PackDroid Ransomware Detector (App) and Dataset | PRA Lab. URL: http:// pralab.diee.unica.it/en/RPackDroid, (Last Accessed: 2023-02-23).
[63] Prachi, Kumar, S., 2022. An effective ransomware detection approach in a cloud environment using volatile memory features. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques URL: https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11416-022-00425-2, doi:10.1007/s11416-022-00425-2.
[64] Sai, R.L.P., Kumar, T.P., 2019. Reverse Engineering the Behaviour of NotPetya Ransomware. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering , 574–578URL: https://www.ijrte.org/wp-content/ uploads/papers/v7i6s/F03120376S19.pdf.
[65] Salehi, S., Shahriari, H., Ahmadian, M.M., Tazik, L., 2018a. A Novel Approach for Detecting DGA-based Ransomwares. 2018 15th International ISC (Iranian Society of Cryptology) Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, ISCISC 2018 doi:10.1109/ISCISC.2018. 8546941.
[66] Salehi, S., Shahriari, H., Ahmadian, M.M., Tazik, L., 2018b. A Novel Approach for Detecting DGA-based Ransomwares, in: 2018 15th International ISC (Iranian Society of Cryptology) Conference on Information Security and Cryptology (ISCISC), pp. 1–7. doi:10.1109/ ISCISC.2018.8546941.
[67] Scaife, N., Carter, H., Traynor, P., Butler, K.R., 2016a. CryptoLock (and Drop It): Stopping Ransomware Attacks on User Data. 2016 IEEE 36th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS) , 303–312URL: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDCS.2016. 46, doi:10.1109/ICDCS.2016.46.
[68] Scaife, N., Carter, H., Traynor, P., Butler, K.R., 2016b. CryptoLock (and Drop It): Stopping Ransomware Attacks on User Data. Proceedings - International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems 2016-Augus, 303–312. doi:10.1109/ICDCS.2016.46.
[69] Shannon, C., 1948. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell System Technology 27, 379–423. URL: https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x, doi:10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338. x.
[70] Sheen, S., Asmitha, K.A., Venkatesan, S., 2022. R-Sentry: Deception based ransomware detection using file access patterns. Computers and Electrical Engineering 103, 108346. URL: https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.compeleceng.2022.108346, doi:10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.108346.
[71] Song, S., Kim, B., Lee, S., 2016. The Effective Ransomware Prevention Technique Using Process Monitoring on Android Platform. Mobile Information Systems 2016, 2946735. URL: https://doi.org/ 10.1155/2016/2946735, doi:10.1155/2016/2946735.
[72] The Telegraph Media Group, 2023. Royal Mail turned down £66m ransom demand from Lockbit hackers. URL: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/business/2023/02/14/ royal-mail-turned-66m-ransom-demand-lockbit-hackers/.
[73] VandenBrink, R., 2016. Using File Entropy to Identify "Ransomwared" Files. URL: https://isc.sans.edu/forums/diary/Using+ FileEntropy+to+Identify+Ransomwared+Files/21351/, (Last Accessed: 2020-09-05).
[74] Walker, J., 2008. Pseudorandom Number Sequence Test Program. URL: https://www.fourmilab.ch/random/, (Last Accessed: 2022-05-29).
[75] Wikipedia, a. List of file formats. URL: https://en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/List_of_file_formats, (Last Accessed: 2022-01-11).
[76] Wikipedia, b. List of file signatures. URL: https://en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/List_of_file_signatures, (Last Accessed: 2022-01-20).
[77] Yamany, B., Elsayed, M.S., Jurcut, A.D., Abdelbaki, N., Azer, M.A., 2022. A New Scheme for Ransomware Classification and Clustering Using Static Features. Electronics (Switzerland) 11. doi:10.3390/ electronics11203307.
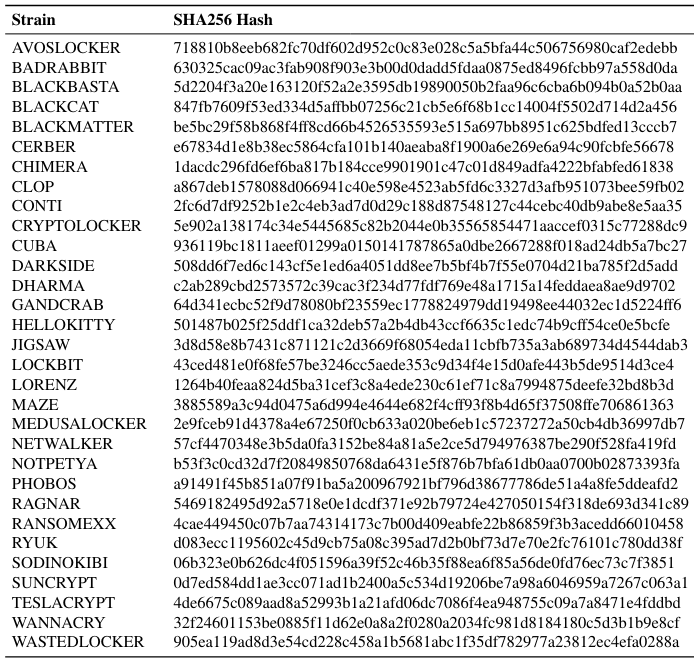
Appendix A Ransomware Strains
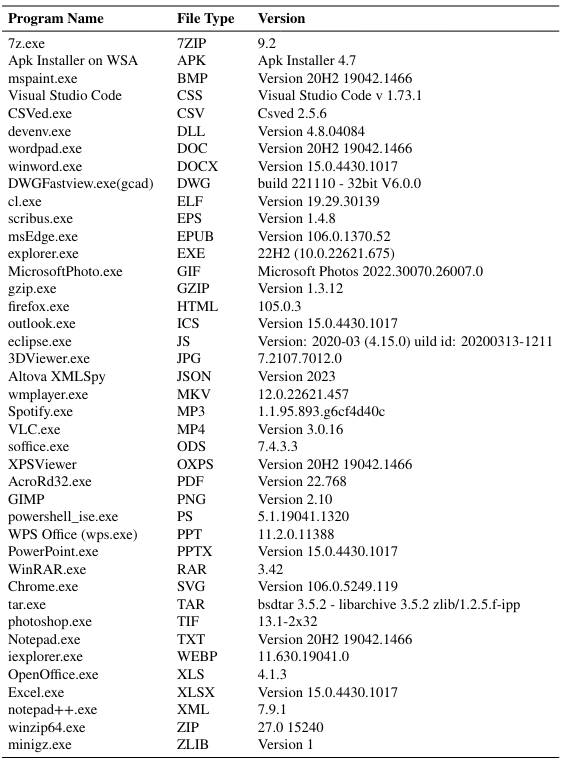
Appendix B Program Information
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.

